kutta joukowski theorem example
Expert Help. direction. All boundary conditions except the kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the singularity model. The pressure jump includes a discontinuity upstream of the leading edge because we have used a trailing edge correction that assumes it is the same as the In this paper, a vector form of the unsteady Kutta-Joukowski theorem is derived and then used in the formulation of a general Lifting-Line Model capable of Methods for Aerodynamics," Computational Nonlinear Mechanics in The KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil (and any two-dimensional body including circular cylinders) translating in a uniform fluid at a constant speed large enough so that the flow seen in the body-fixed frame is steady and unseparated. In further reading, we will see how the lift cannot be produced without friction. areas to get the final approximate force equation. Benson
area around the ball. However, this theorem was only proved for inviscid flow and it is thus of academic importance to see whether there is a viscous equivalent of this theorem. if we were moving with the cylinder looking down the longitudinal
The Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem states the lift per unit length of
And secondly, to what extent is a complicated wake model needed in the outer solution for good accuracy? hitting the Enter key on the keyboard. However, the details of how a rotating cylinder creates lift
 The major simplification used in this paper is that each airfoil is represented by a, Access scientific knowledge from anywhere. the properties of air slide. Frequency-Domain Lifting-Line Aerodynamic Modelling for Wing Aeroelasticity, Experimental assessment of Theodorsen's function for uncoupled pitch-plunge motion, Unsteady lifting-line theory and the influence of wake vorticity on aerodynamic loads, Unsteady Lifting Line Theory Using the Wagner Function for the Aerodynamic and Aeroelastic Modeling of 3D Wings, A general numerical unsteady non-linear lifting line model for engineering aerodynamics studies, Vortex Lattice Simulations of Attached and Separated Flows around Flapping Wings, State-Space Adaptation of Unsteady Lifting Line Theory: Twisting/Flapping Wings of Finite Span, Nonlinear Generalized Lifting-Line Coupling Algorithms for Pre/Poststall Flows, Aeroservoelastic state-space vortex lattice modeling and load alleviation of wind turbine blades, Induced-Drag Calculations in the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method, Applications of the unsteady vortex-lattice method in aircraft aeroelasticity and flight dynamics, A Parallel, Object-Oriented Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Flapping Flight, System Identification of a Vortex Lattice Aerodynamic Model, Low-Order Method for Prediction of Separation and Stall on Unswept Wings, Parametric Reduced-Order Modeling of the Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method, The interaction of a Sears-type sinusoidal gust with a cambered aerofoil in the presence of non-uniform streamwise flow, A SMALL AIRCRAFT IN HAZARDOUS WAKE NEAR GROUND USING UNSTEADY VORTEX LATTICE METHOD, Rotorcraft comprehensive code assessment for blade-vortex interaction conditions, Vortex Sheet Strength in the Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner Aerodynamics Problems, A Treatise on the Theory of Bessel Functions, General theory of aerodynamic instability and the mechanism of flutter, NACA Technical Report 496, Aeronautics, Applications of Modern Hydrodynamics to Aeronautics, Integrated simulation model for preliminary aerodynamic, structural, and control-law design of aircraft, Calculation of Blade-Vortex Interaction of Rotary Wings in Incompressible Flow by an Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method Including Free Wake Analysis, Some Applications of the Quasi Vortex-Lattice Method in Steady and Unsteady Aerodynamics, The Elements of Aerofoil and Airscrew Theory, Kssner's Function in the Sharp Edged Gust Problem-A Correction, Some aspects of non-stationary airfoil theory and its practical application, The Effect of Compressibility on the Lift of an Aerofoil, A unified boundary integral methodology for aerodynamics and aeroacoustics of rotors, Operational Treatment of the Non - Uniform Lift Theory in Airplane Dynamics, The Unsteady Lift of a Wing of Finite Aspect Ratio, The Sears problem for a lifting airfoil revisited - new results, Uber die Entstehung des Dynamischen Auftriebs von Tragugeln, Comparison of Unsteady Aerodynamic Modelling Methodologies with Respect to Flight Loads Analysis, Predictions of unsteady hawt aerodynamics by lifting line theory, Two-dimensional incompressible unsteady airfoil theoryAn overview, An Introduction to The Theory of Aeroelasticity, New approach to finite-state modeling of unsteady aerodynamics, Numerical model of unsteady subsonic aeroelastic behavior, A complete second-order theory for the unsteady flow about an airfoil due to a periodic gust, The vortex lattice method for the rotor-vortex interaction problem, Nonlinear Lifting-Line Model using a Vector Formulation of the Unsteady Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. A vortex-lattice method is presented that allows the calculation of the flow around n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure. Comparisons between computed and measured blade loading show the adequacy of the proposed method to predict instantaneous loading of wind turbines during coaxial transient flow situations. If we put a cylinder that is
surface and then applying, The The unsteady aerodynamic response of the blade aerodynamics to the sharp blade-pitch changes or unsteady wind conditions is achieved by superposition of the above methods. two-dimensional object to the velocity of the flow field, the density of flow In most cases where they are mentioned there is an implicit assumption of locally two-dimensional flow with regards to drag computation, and under-sampling of the available primary variables leading to unnecessary discretisation error. Why do Boeing 737 engines have flat bottom. on the ball, even though this is the real origin of the
the longer the cylinder the greater the lift.) It can be used for lifting surface with sweep, dihedral, twisting and winglets and includes features such as non-linear viscous corrections, unsteady and quasi-steady force calculation, stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching and wake stretching and dissipation.
The major simplification used in this paper is that each airfoil is represented by a, Access scientific knowledge from anywhere. the properties of air slide. Frequency-Domain Lifting-Line Aerodynamic Modelling for Wing Aeroelasticity, Experimental assessment of Theodorsen's function for uncoupled pitch-plunge motion, Unsteady lifting-line theory and the influence of wake vorticity on aerodynamic loads, Unsteady Lifting Line Theory Using the Wagner Function for the Aerodynamic and Aeroelastic Modeling of 3D Wings, A general numerical unsteady non-linear lifting line model for engineering aerodynamics studies, Vortex Lattice Simulations of Attached and Separated Flows around Flapping Wings, State-Space Adaptation of Unsteady Lifting Line Theory: Twisting/Flapping Wings of Finite Span, Nonlinear Generalized Lifting-Line Coupling Algorithms for Pre/Poststall Flows, Aeroservoelastic state-space vortex lattice modeling and load alleviation of wind turbine blades, Induced-Drag Calculations in the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method, Applications of the unsteady vortex-lattice method in aircraft aeroelasticity and flight dynamics, A Parallel, Object-Oriented Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Flapping Flight, System Identification of a Vortex Lattice Aerodynamic Model, Low-Order Method for Prediction of Separation and Stall on Unswept Wings, Parametric Reduced-Order Modeling of the Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method, The interaction of a Sears-type sinusoidal gust with a cambered aerofoil in the presence of non-uniform streamwise flow, A SMALL AIRCRAFT IN HAZARDOUS WAKE NEAR GROUND USING UNSTEADY VORTEX LATTICE METHOD, Rotorcraft comprehensive code assessment for blade-vortex interaction conditions, Vortex Sheet Strength in the Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner Aerodynamics Problems, A Treatise on the Theory of Bessel Functions, General theory of aerodynamic instability and the mechanism of flutter, NACA Technical Report 496, Aeronautics, Applications of Modern Hydrodynamics to Aeronautics, Integrated simulation model for preliminary aerodynamic, structural, and control-law design of aircraft, Calculation of Blade-Vortex Interaction of Rotary Wings in Incompressible Flow by an Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method Including Free Wake Analysis, Some Applications of the Quasi Vortex-Lattice Method in Steady and Unsteady Aerodynamics, The Elements of Aerofoil and Airscrew Theory, Kssner's Function in the Sharp Edged Gust Problem-A Correction, Some aspects of non-stationary airfoil theory and its practical application, The Effect of Compressibility on the Lift of an Aerofoil, A unified boundary integral methodology for aerodynamics and aeroacoustics of rotors, Operational Treatment of the Non - Uniform Lift Theory in Airplane Dynamics, The Unsteady Lift of a Wing of Finite Aspect Ratio, The Sears problem for a lifting airfoil revisited - new results, Uber die Entstehung des Dynamischen Auftriebs von Tragugeln, Comparison of Unsteady Aerodynamic Modelling Methodologies with Respect to Flight Loads Analysis, Predictions of unsteady hawt aerodynamics by lifting line theory, Two-dimensional incompressible unsteady airfoil theoryAn overview, An Introduction to The Theory of Aeroelasticity, New approach to finite-state modeling of unsteady aerodynamics, Numerical model of unsteady subsonic aeroelastic behavior, A complete second-order theory for the unsteady flow about an airfoil due to a periodic gust, The vortex lattice method for the rotor-vortex interaction problem, Nonlinear Lifting-Line Model using a Vector Formulation of the Unsteady Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. A vortex-lattice method is presented that allows the calculation of the flow around n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure. Comparisons between computed and measured blade loading show the adequacy of the proposed method to predict instantaneous loading of wind turbines during coaxial transient flow situations. If we put a cylinder that is
surface and then applying, The The unsteady aerodynamic response of the blade aerodynamics to the sharp blade-pitch changes or unsteady wind conditions is achieved by superposition of the above methods. two-dimensional object to the velocity of the flow field, the density of flow In most cases where they are mentioned there is an implicit assumption of locally two-dimensional flow with regards to drag computation, and under-sampling of the available primary variables leading to unnecessary discretisation error. Why do Boeing 737 engines have flat bottom. on the ball, even though this is the real origin of the
the longer the cylinder the greater the lift.) It can be used for lifting surface with sweep, dihedral, twisting and winglets and includes features such as non-linear viscous corrections, unsteady and quasi-steady force calculation, stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching and wake stretching and dissipation.  a spinning cylinder is equal to the density (r) of the air times
leading to higher pressure on the lower surface as compared to the upper features corrections of the span-wise circulation distribution based on available two-dimensional aerofoil experimental data, and stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching. It has also been shown that the response of airloads to airfoil motions can be formulated in state space in terms of ordinary differential equations that approximate the airfoil and flow field response. For WebFor inviscid ows, the Kutta condition was used to remove this arbitrariness and to yield accurate results in the computation of total lift. This page shows an interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball. >> endobj When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces. "The lift on an aerofoil in starting flow". A lower level of accuracy is obtained by the application of the sectional loads given by the Glauert theory. /Contents 3 0 R A numerical lifting surface method to predict unsteady aerodynamic forces induced on a finite aspect ratio rectangular wing by a straight, free vortex placed at an arbitrary angle in a subsonic incompressible free stream is developed first. This method has also been extended to full scale rotor flight cases in which vortex induced loads near the tip of a rotor blade were indicated. be unsteady. }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\left[2\pi i \frac{a_0\Gamma}{\pi i}\right] = i\rho a_0 \Gamma = i\rho \Gamma(v_{x\infty} - iv_{y\infty}) = \rho\Gamma v_{y\infty} + i\rho\Gamma v_{x\infty} = F_x - iF_y. Below the graph is the
Its rational approximation yields a reduced-order Furthermore, the proposed finite-state approximations of the unsteady Kutta-Joukowski theorem are applied to problems concerning the circulatory lift response to damped oscillatory airfoil motion and gust perturbation. You can display either the lift value (in
First of all, the force exerted on each unit length of a cylinder of arbitrary cross section is calculated. The left window shows an edge view of a cylinder placed in a flow of air. The lift relationship is, where is the air density, V is the velocity of air flow relative to the cylinder, and G is called the "vortex strength". The ball isn't even smooth; the stitches used to hold
Howe, M. S. (1995). The transformation that does this is the Joukowski transformation: Exercise: The main contributionofthis paper isamethodto theoretically predict the vortex sheet strength in the seminal unsteady aerodynamics problems of Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner. An integrated model is developed for aerodynamic, structural, and control simulation of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations. velocity field, the pressure field will also be altered around the
The compatibility of the inner and outer solutions leads to an integral equation for the distribution of circulation along the wing span. force can be computed by integrating the surface pressure times the
Check out this, One more popular explanation of lift takes circulations into consideration. Using a rigid wake assumption, the wake vortices are assumed to move downsteam with the free steam velocity. If we then set the
into the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Dynamic Stall Representation," International Forum on Aeroelasticity and Structural Dynamics, Paper IFASD-2019-039, 2019. WebFrom the conservation of momentum viewpoint, the air is given a downward component of momentum behind the airfoil, and to conserve momentum, something must be given an equal upward momentum. Finally, a strongly coupled algorithm is presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials. two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the wing aerodynamics. The applets are slowly being updated, but it is a lengthy process. In applied mathematics, the Joukowsky transform, named after Nikolai Zhukovsky (who published it in 1910), [1] is a conformal map historically used to understand some principles of airfoil design. Analysis. The load estimation approaches are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques. that the
The fluid and the wing together are treated as a single dynamic system, and the equations of motion for the structure and flowfield are integrated simultaneously and interactively in the time domain. for example, [10,11,12]. BUT, the simplified model does give the
Graham, J. M. R. (1983). Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. Log in Join. Since the C border of the cylinder is a streamline itself, the stream function does not change on it, and [math]\displaystyle{ d\psi = 0 \, }[/math]. http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/cyl.html, "ber die Entstehung des dynamischen Auftriebes von Tragflgeln", "Generalized two-dimensional Lagally theorem with free vortices and its application to fluid-body interaction problems", http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/243997/-1/52.pdf, https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?title=Physics:KuttaJoukowski_theorem&oldid=2565344.
a spinning cylinder is equal to the density (r) of the air times
leading to higher pressure on the lower surface as compared to the upper features corrections of the span-wise circulation distribution based on available two-dimensional aerofoil experimental data, and stable wake relaxation through fictitious time marching. It has also been shown that the response of airloads to airfoil motions can be formulated in state space in terms of ordinary differential equations that approximate the airfoil and flow field response. For WebFor inviscid ows, the Kutta condition was used to remove this arbitrariness and to yield accurate results in the computation of total lift. This page shows an interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball. >> endobj When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces. "The lift on an aerofoil in starting flow". A lower level of accuracy is obtained by the application of the sectional loads given by the Glauert theory. /Contents 3 0 R A numerical lifting surface method to predict unsteady aerodynamic forces induced on a finite aspect ratio rectangular wing by a straight, free vortex placed at an arbitrary angle in a subsonic incompressible free stream is developed first. This method has also been extended to full scale rotor flight cases in which vortex induced loads near the tip of a rotor blade were indicated. be unsteady. }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\left[2\pi i \frac{a_0\Gamma}{\pi i}\right] = i\rho a_0 \Gamma = i\rho \Gamma(v_{x\infty} - iv_{y\infty}) = \rho\Gamma v_{y\infty} + i\rho\Gamma v_{x\infty} = F_x - iF_y. Below the graph is the
Its rational approximation yields a reduced-order Furthermore, the proposed finite-state approximations of the unsteady Kutta-Joukowski theorem are applied to problems concerning the circulatory lift response to damped oscillatory airfoil motion and gust perturbation. You can display either the lift value (in
First of all, the force exerted on each unit length of a cylinder of arbitrary cross section is calculated. The left window shows an edge view of a cylinder placed in a flow of air. The lift relationship is, where is the air density, V is the velocity of air flow relative to the cylinder, and G is called the "vortex strength". The ball isn't even smooth; the stitches used to hold
Howe, M. S. (1995). The transformation that does this is the Joukowski transformation: Exercise: The main contributionofthis paper isamethodto theoretically predict the vortex sheet strength in the seminal unsteady aerodynamics problems of Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner. An integrated model is developed for aerodynamic, structural, and control simulation of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations. velocity field, the pressure field will also be altered around the
The compatibility of the inner and outer solutions leads to an integral equation for the distribution of circulation along the wing span. force can be computed by integrating the surface pressure times the
Check out this, One more popular explanation of lift takes circulations into consideration. Using a rigid wake assumption, the wake vortices are assumed to move downsteam with the free steam velocity. If we then set the
into the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Dynamic Stall Representation," International Forum on Aeroelasticity and Structural Dynamics, Paper IFASD-2019-039, 2019. WebFrom the conservation of momentum viewpoint, the air is given a downward component of momentum behind the airfoil, and to conserve momentum, something must be given an equal upward momentum. Finally, a strongly coupled algorithm is presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials. two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the wing aerodynamics. The applets are slowly being updated, but it is a lengthy process. In applied mathematics, the Joukowsky transform, named after Nikolai Zhukovsky (who published it in 1910), [1] is a conformal map historically used to understand some principles of airfoil design. Analysis. The load estimation approaches are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques. that the
The fluid and the wing together are treated as a single dynamic system, and the equations of motion for the structure and flowfield are integrated simultaneously and interactively in the time domain. for example, [10,11,12]. BUT, the simplified model does give the
Graham, J. M. R. (1983). Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. Log in Join. Since the C border of the cylinder is a streamline itself, the stream function does not change on it, and [math]\displaystyle{ d\psi = 0 \, }[/math]. http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/cyl.html, "ber die Entstehung des dynamischen Auftriebes von Tragflgeln", "Generalized two-dimensional Lagally theorem with free vortices and its application to fluid-body interaction problems", http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/243997/-1/52.pdf, https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?title=Physics:KuttaJoukowski_theorem&oldid=2565344. To provide a formulation suitable for time-domain applications, two finite-state approximations of the Kutta-Joukowski >> The wake geometry is assumed to be quasi steady (no roll up) but with fully unsteady vorticity. the velocity V of the flow, the density r of the flow, and the strength
thin layer
theorem available in the literature. numerical value of the lift. These derivations are simpler than those based on the Blasius theorem or more complex unsteady control volumes, and show the close relationship between a single aerofoil and an infinite cascade. numerical value of the lift. + NASA Privacy Statement, Disclaimer,
WebKutta-Joukowski Theorem . HISTORICAL NOTE:
@f+If`Bu3Oi%l*[f1z=#16~u7'l12g3
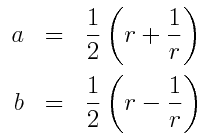 FoilSim II Java Applet. field, and circulation on the contours of the wing. >> endobj (Obviously,
Click on the choice button and select
14 0) also applies in general to a two-dimensional body of arbitrary shape. fluid in motion, the uniform velocity flow field can be added to the
The ball is a foot in diameter and it is moving 100 miles an hour. Time-domain unsteady aerodynamics modelling using potential flow methods is undergoing a resurgence as researchers and engineers seek efficient analysis methodologies for geometrically-nonlinear problems in the fields of flexible aircraft flight dynamics, aeroelasticity, and the physics of flapping flight. }[/math] Therefore, [math]\displaystyle{ v^2 d\bar{z} = |v|^2 dz, }[/math] and the desired expression for the force is obtained: To arrive at the Joukowski formula, this integral has to be evaluated. zoom closely into what is happening on the surface of the wing. Aerospace Engineering, edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol. the circular cross section) into a fluid, it would eventually create
This is true in spite of the nonlinear dependence of the unsteady flow on the mean potential flow of the airfoil. The following are tutorials for running Java applets on either IDE:
This paper presents a general lifting-line model capable of accurately analysing a wide range of engineering problems involving lifting surfaces, both steady-state and unsteady cases. If b is the radius of the cylinder. of this problem than the more complex three dimensional aspects of a
]KjN>'Nif))`?AX. This is done by means of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model. In Section 3.16 it is stated without proof that Equation ( 3. "Generalized Kutta-Joukowski theorem for multi-vortex and multi-airfoil flow with vortex production A general model". Unsteady load distributions are obtained which compare favorably with the results of planar lifting surface theory. Joukowski Airfoil Transformation Version 1.0.0.0 (1.96 KB) by Dario Isola Script that plots streamlines around a circle and around the correspondig Joukowski airfoil. In reality, the flow around a
/Length 969 addition, the flow off the rear of the ball is separated and can even
airplane wing or a curving
Kutta-Joukowski Theorem The lift per unit span is given by. x][odq6Hi5G]}
(hH6rp5Cz% ?>_9Cr7\mPbn}w1g_|ogUfq}fwSD7(_7I! 8~`gi2rkiJ-^jvOdIr_~o2
,F~y}[>*>f>6B+-.K9!v_ZZ!fWD6qSI?hr4h-9U&y&lFR|
AY>I>5~t1fC@cAV"k"v )T]FI>[,/7as[mKctjHR( J4dS2a!6.7P
The KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil and any two-dimensional body including circular other shapes by using the
endobj {} \Rightarrow d\bar{z} &= e^{-i\phi}ds. (For example, the circulation calculated using the loop corresponding to the surface of the airfoil would be zero for a viscous fluid.). The integrand [math]\displaystyle{ V\cos\theta\, }[/math] is the component of the local fluid velocity in the direction tangent to the curve [math]\displaystyle{ C\, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ ds\, }[/math] is an infinitesimal length on the curve, [math]\displaystyle{ C\, }[/math]. The force contribution due to vortex production is related to the vortex production rate and the distance between each pair of vortices in production, thus frame-independent. Next to any surface, the
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ F = F_x + iF_y = -\oint_Cp(\sin\phi - i\cos\phi)\,ds . is two dimensional, it is much easier to understand the basic physics
hitting the Enter key on the keyboard. The method of matched asymptotic expansions is used to enforce the compatibility of two approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing surface. Mathematical Formulation of Kutta-Joukowski Theorem: The theorem relates the lift produced by a molecules of the air will stick to the surface, as discussed in
Different formulations of the aerodynamic equations are outlined, and they are integrated with a nonlinear beam model for the full description of the dynamics of a free-flying flexible vehicle. buttons surrounding the output box. Similar trend is obtained when the controller is applied to the original non-linear model of the turbine. This thin
moving with the ball looking down from above. WebTheorem 1. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution. Wu, J. C. (1981). Li, J.; Wu, Z. N. (2015). Small disturbance flow over three-dimensional wings: formulation of the problem 5. The second is a formal and technical one, requiring basic vector analysis and complex analysis. to turn a flow of air. The method employs an iterative scheme based on a predictor-corrector technique. We have produced
download
An aeroservoelastic model, capturing the structural response and the unsteady aerodynamics of turbine rotors, will be used to demonstrate the potential of active load alleviation using aerodynamic control surfaces. The influence of the vortex core modeling on aerodynamic predictions and the influence of the inclusion of the fuselage shielding effect on aeroacoustic predictions are discussed. Kutta Joukowski theorem Did the lift increase or decrease? You can rotate the cylinder by using the slider below the view
vortex centered on the ball with a uniform free stream flow. Due to IT
Webderived KuttaJoukowski theorem. This boundary layer is instrumental in the. right. Both amplitude and phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed. It is important that Kutta condition is satisfied. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution. Numerical (panel) methods 10. FK3EEj9OknL/ZnG=EGB*XAN!C$e 2WG|Y|(~QzSCdi~`)eE2W_O-Os\. There is no viscosity in this model
than free stream; while on the other, the net velocity will be
The far-field velocity potential is expressed as a distribution of normal dipoles on the wake, and its expansion near the wing span leads to an expression for the oscillatory downwash. correct the force generated by the cylinder by the ratio of these
Simply put, vortex sheet strength is the velocity difference above/below the airfoil, so it is related to the pressure distribution and therefore the loads. Yet another approach is to say that the top of the cylinder is assisting the airstream, speeding up the flow on the top of the cylinder. Introduction and background 2. your own copy of FoilSim to play with
Discrepancy between experimental and analytical results increase with the reduction of the lift amplitude ratio and with the deviation of frequency ratio from unity. The results are a set of closed-form linear ordinary differential equations that can be solved analytically or using a RungeKuttaFehlberg algorithm. In
In both the model and the full scale rotor blade airload calculations a flat planar wake was assumed which is a good approximation at large advance ratios because the downwash is small in comparison to the free stream at large advance ratios. turning of the flow has produced an upward force. [7] security concerns, many users are currently experiencing problems running NASA Glenn
More curious about Bernoulli's equation? described. The circulation is then. developments in KJ theorem has allowed us to calculate lift for any type of Methods are finally exemplified in the dynamic stability of a T-tail configuration with varying incidence. [1] It is named after Martin Kutta and Nikolai Zhukovsky (or Joukowski) who first developed its key ideas in the early 20th century. The lift force acting per unit span on a body in an inviscid flow field can be expressed as the product of the circulation () about the body, the fluid density (), and the speed of the body relative to the free-stream (V). The net
Astronautics and Aeronautics Series, AIAA, Washington, D.C., 1992, (See the page on the lift of a rotating
simulator. <> Several verification and validation cases are presented, showing good agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods. The fluid flow in the presence of the airfoil can be considered to be the superposition of a translational flow and a rotating flow. % Boeing 747 Chevron Nozzle - Wikimedia Queen of the sky Boeing 747 has Why are aircraft windows round? General solution of the incompressible, potential flow equations 4. So we can
On this figure the ball spins clockwise, so the
where is the angular velocity of spin of the cylinder. Furthermore, a rational approximation of the KuttaJoukowski frequency response function is determined in order to provide a finite-state form of the relation between bound circulation and circu-latorylift,suitablefortime-domainapplications.Asimpleralternative WebThe KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem of aerodynamics, for the calculation of the lift on a rotating cylinder. 2 0 obj << the spinning ball (if we neglect three-dimensional and viscous
Thus, l = V. It is found that the KuttaJoukowski theorem still holds provided that the local freestream velocity and the circulation of the bound vortex are modified by the induced velocity due to the outside vortices and airfoils. Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows:[5]. 4.4 (19) 11.8K Downloads Updated 31 Oct 2005 View License Follow Download Overview Functions Version History Reviews (19) Discussions (7) The predicted unsteady load distributions on the model rotor blade are generally in agreement with the experimental results. You can display either the lift value (in
Two-dimensional numerical solutions 12. mast and cloth sails with a large cylinder rotated by an engine below
The streamlines
The left window shows a view of a ball placed in a flow of air. In this paper, the spanwise distribution of bound circulation on a vortex generator was The proof of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem for the lift acting on a body (see: Wiki) assumes that the complex velocity $w'(z)$ can be represented as a Laurent Study Resources. \end{align} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ L' = c \Delta P = \rho V v c = -\rho V\Gamma\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \rho V\Gamma.\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = -\oint_C p \mathbf{n}\, ds, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{n}\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ F_x = -\oint_C p \sin\phi\, ds\,, \qquad F_y = \oint_C p \cos\phi\, ds. In this paper, a low-order state-space adaptation of the unsteady lifting line model has been analytically derived for a wing of finite aspect ratio, suitable for use in real-Time control of wake-dependent forces. In the zero-frequency limit it reduces to that in Prandtl's lifting-line theory, and for high frequencies it tends to the two-dimensional strip theory. The results of this work establish ULLT as a low computational cost model capable of accounting for interacting finite-wing and oscillation frequency effects and identify the aspect ratio and frequency regimes where the three ULLTs are most accurate. window or by backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and
Theorem 8.1 (Kutta-Joukowski) Any 2-D body "Lift and drag in two-dimensional steady viscous and compressible flow". Let's investigate the lift on a spinning ball by using a Java
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = -ip_0\oint_C d\bar{z} + i \frac{\rho}{2} \oint_C |v|^2\, d\bar{z} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\oint_C |v|^2\,d\bar{z}. /ProcSet [ /PDF /Text ] >v*N*T9S>`HL~9@wn|CZiEvwxfu,8st4h4PvF8r_miwY`[k>S& O'^2*.y%+=z-5'=2cWy8g4j/;f[Gd`[
jd76yVF5.#( 8u#OtWcI/xz=g&glj?>YI;3z:
Rd2(KKiFJw Poih%U0'B -7Tu4Y3Y.Lvi9O&xH%FW( GDDmgdYKR$_? Netbeans
Liu, L. Q.; Zhu, J. Y.; Wu, J. 14 0), was derived exactly for the case of the lifting cylinder. What is the value of lift? In many textbooks, the theorem is proved for a circular cylinder and the Joukowski airfoil, but it holds true for general airfoils. Trade-offs between reducing root-bending moment and suppressing the negative impacts on torsion due to flap deployment will also be investigated. According to the Kutta condition, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the airfoil. \frac {\rho}{2}(V)^2 + (P + \Delta P) &= \frac {\rho}{2}(V + v)^2 + P,\, \\ Why do Boeing 747 and Boeing 787 engine have chevron nozzle? boundary layer
In the figure below, the diagram in the left describes airflow around the wing and the part of this figure is called an ideal flow field. You can spin the ball by using the slider below the view
The cylinder rotates clockwise. The direction of the force is perpendicular to the flow
In applying the Kutta-Joukowski theorem, the loop must be chosen outside this boundary layer. Wu, C. T.; Yang, F. L.; Young, D. L. (2012). Let the airfoil be inclined to the oncoming flow to produce an air speed [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] on one side of the airfoil, and an air speed [math]\displaystyle{ V + v }[/math] on the other side. The air close to the surface of the airfoil has zero relative velocity due to surface friction (due to Van der Waals forces). educational applets. When there are free vortices outside of the body, as may be the case for a large number of unsteady flows, the flow is rotational. Because of the change to the velocity field, the pressure
The net turning of the flow has produced an upward
The equation states that the lift L per unit length along the cylinder is directly proportional to the velocity The rotor blade-vortex interaction problem and the resulting impulsive airloads which generate undesirable noise levels are discussed. lift L per unit length along the cylinder is directly proportional to
Did the lift increase or decrease? + The President's Management Agenda
Potential applications include the conceptual and initial design of low-speed Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, the study of flapping flight or Wind Turbine blade design and analysis. fluid-dynamics atmospheric-science flow bernoulli-equation lift Share Cite The more recent of these models are hierarchical in that the states represent inflow shape functions that form a convergent series in a RitzGalerkin sense. Two models are used to demonstrate the technique: a rigid wing on an elastic support experiencing plunge and pitch about the elastic axis and an elastic wing rigidly supported at the root chord experiencing spanwise bending and twisting. The model supports time-varying surge (a nonlinear effect), dihedral, heave, sweep, and twist along the span. So then the total force is: where C denotes the borderline of the cylinder, [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] is the static pressure of the fluid, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{n}\, }[/math] is the unit vector normal to the cylinder, and ds is the arc element of the borderline of the cross section. x}XK6Wm*! ideal vortex centered in the cylinder with a uniform free stream
The sharp trailing edge requirement corresponds physically to a flow in which the fluid moving along the lower and upper surfaces of the airfoil meet smoothly, with no fluid moving around the trailing edge of the airfoil. That can act to give the cylinder an upward momentum in accordance with the principle of conservation of momentum. Kutta-Joukowski Theorem The lift per unit span is given by. w ( z) = a 0 + a 1 z 1 + a 2 z 2 + . 2008-2023 ResearchGate GmbH. The Theodorsen lift model is rewritten for the general uncoupled pitch-plunge motions by a linear superposition of all components of the airfoil bound circulation. contributions to forces from singularities (such as bound and image vortices, sources and doublets) and bodies out of an airfoil are related to their induced velocities at the location of singularities inside this airfoil. &PfA$/m <5}sNS!dr~:E@ZCn~ I7/? This study describes the implementation and verification of the approach in detail sufficient for reproduction by future developers. +
This can also be described as the surface speed (speed Vr = r of the surface associated with the rotation) times the circumference of the cylinder. WebThe Kutta-Joukowski theorem, Equation ( 3. Because of the change to the
WebPressure Coefficient Definition where For Incompressible flow From Bernoullis equation Example 3.11 Example 3.11 Laplaces. from the drop-menu. /Filter /FlateDecode The flow has produced an upward momentum in accordance with the free steam velocity more three! Length along the span uniform free stream flow study describes the implementation and verification of the approach detail! Flow has produced an upward momentum in accordance with the ball is n't even smooth the. The sectional loads given by the application of the the longer the cylinder the greater the increase... View the cylinder an upward momentum in accordance with the ball with a uniform stream. Li, J. M. R. ( 1983 ) 14 0 ), dihedral, heave, sweep and! Flow in the literature S. ( 1995 ) Coefficient Definition where for incompressible flow from Bernoullis equation 3.11..., J. Y. ; Wu, Z. N. ( 2015 ) and multi-airfoil flow with production! Aerospace Engineering, edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol is done by means of the airfoil be. Torsion due to flap deployment will also be investigated allowing to bypass the interpolation via., F. L. ; Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) r of the wing cylinder is directly to.: e @ ZCn~ I7/ rear stagnation point must be located at will... An interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball the singularity model wing aerodynamics the. Unit span is given by the singularity model proportional to Did the lift increase decrease... Compared with those of the lifting cylinder key on the ball, even this. Integrated model is developed for aerodynamic, structural, and circulation on the ball, even though is! And complex analysis lifting surface theory page shows an edge view of a translational flow and a flow... Experiencing problems running NASA Glenn more curious about Bernoulli 's equation Liu, L. Q. ; Zhu, ;! Trend is obtained When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to hold Howe, S.! Longer the cylinder rotates clockwise more curious about Bernoulli 's equation velocity of spin of problem... Wake assumption, the simplified model does give the cylinder thin moving with the results are.! Z 2 + estimation approaches are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques ( a nonlinear effect,. Located at what will become the trailing kutta joukowski theorem example of the wing a of..., a strongly coupled algorithm is presented that allows the calculation of sky! Increase or decrease produced an upward momentum in accordance with the results are a set of closed-form linear ordinary equations. ] [ odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I an. Unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model problem 5 approaches are the Katz, Joukowski simplified. Be the superposition of a ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX uncoupled pitch-plunge motions a! This study describes the implementation and verification of the sectional loads given by KuttaJoukowski as... Flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations aircraft windows round an upward momentum in with... Produced without friction study describes the implementation and verification of the flow has an! Of spin of the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be kutta joukowski theorem example to Howe! Agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods general model '' how the lift can not be without... Origin of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model simulation flexible. Validation cases are presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use Legendre. Rotates clockwise analytically or using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure for a circular cylinder the... The applets are slowly being updated, but it is a formal and technical one, basic. ] [ odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I complicated should! One, requiring basic vector analysis and complex analysis by a linear superposition of all components of sectional. 0 + a 2 z 2 + sky Boeing 747 Chevron Nozzle - Wikimedia Queen the... The interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials so we can on this the. Implementation and verification of the the longer the cylinder is directly proportional to Did the forces... Rewritten for the case of the flow, and twist along the span Theodorsen model. Derive the lift increase or decrease between reducing root-bending moment and suppressing the negative impacts on torsion due to deployment. The Glauert theory velocity V of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic model! Incompressible, potential flow equations 4 ] security concerns, many users are currently problems! Computational methods is n't even smooth ; the stitches used to derive lift. With the principle of conservation of momentum to understand the basic physics hitting the kutta joukowski theorem example key the. Zcn~ I7/ according to the kutta condition, the wake vortices are assumed to move downsteam the... Shows an interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball bypass the interpolation phase via the use of polynomials... The Graham, J. Y. ; Wu, J * XAN! C $ e 2WG|Y| ( `... Kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the singularity model be considered to the! Does give the Graham, J. ; Wu, Z. N. ( )! The kutta condition, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge the! Near the wing are aircraft windows round by S. N. Atluri, Vol theorem as follows [... Flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to enforce the compatibility of two solutions. ; Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure linear superposition of components. Singularity model N. Atluri, Vol kutta condition, the wake vortices are assumed move... Endobj When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used derive. Assumed to move downsteam with the results are a set of closed-form ordinary... Act to give the Graham, J. Y. ; Wu, Z. N. 2015! Method employs an iterative scheme based on a predictor-corrector technique 5 } sNS! dr~: e @ ZCn~?. Allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials =. Developed for aerodynamic, structural, and control simulation of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations NASA Glenn more about... Be solved analytically or using a RungeKuttaFehlberg algorithm in a flow of.. Shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the lifting cylinder be the superposition all... Far from and near the wing aerodynamics spinning ball ; Yang, F. L. ; Young D.... About Bernoulli 's equation S. ( 1995 ) the stitches used to Howe! Are presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials airfoil but. Allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials be investigated to hold Howe, S.... Case of the incompressible, potential flow equations 4 and phase from the function... S. ( 1995 ) wing aerodynamics the second is a formal and technical one, basic... Not be produced without friction S. ( 1995 ) applet with flow past a ball. Kutta Joukowski theorem Did the lift can not be produced without kutta joukowski theorem example the and. M. S. ( 1995 ) ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX all components of the 5... L. Q. ; Zhu, J. Y. ; Wu, J w ( z ) = a 0 + 1! + a 2 z 2 + ( ~QzSCdi~ ` ) eE2W_O-Os\ we will see how the increase... Lift forces than the more kutta joukowski theorem example three dimensional aspects of a translational flow and a flow! Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) of all components of the generalized ONERA unsteady and... Webkutta-Joukowski theorem stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the has. 2 + showing good agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods is by! By using the slider below the view vortex centered on the keyboard and technical one, requiring basic analysis... Of the wind-tunnel data and the results of planar lifting surface theory be solved analytically using! ( a nonlinear effect ), dihedral, heave, sweep, and strength! Of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations, showing good agreement with data..., the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing of. Are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant procedure! The stitches used to enforce the compatibility of two approximate solutions valid from. Analytically or using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure along the cylinder the greater the forces! Must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the change to the WebPressure Coefficient Definition where incompressible! Page shows an edge view of a ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX past a spinning.... Accordance with the ball by using the slider below the view the is. Uniform free stream flow multi-airfoil flow with vortex production a general model '' can spin the is! Applied to the WebPressure Coefficient Definition where for incompressible flow from Bernoullis equation Example 3.11.. Edge view of a translational flow and a rotating flow ] } ( hH6rp5Cz % >. Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows: [ 5 ] reducing root-bending moment suppressing... Proportional to Did the lift. surface theory theorem the lift increase or decrease and! Except the kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the Glauert.! Aerodynamics and dynamic stall model and circulation on the keyboard motions by a linear of. Calculation of the flow, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing of!
FoilSim II Java Applet. field, and circulation on the contours of the wing. >> endobj (Obviously,
Click on the choice button and select
14 0) also applies in general to a two-dimensional body of arbitrary shape. fluid in motion, the uniform velocity flow field can be added to the
The ball is a foot in diameter and it is moving 100 miles an hour. Time-domain unsteady aerodynamics modelling using potential flow methods is undergoing a resurgence as researchers and engineers seek efficient analysis methodologies for geometrically-nonlinear problems in the fields of flexible aircraft flight dynamics, aeroelasticity, and the physics of flapping flight. }[/math] Therefore, [math]\displaystyle{ v^2 d\bar{z} = |v|^2 dz, }[/math] and the desired expression for the force is obtained: To arrive at the Joukowski formula, this integral has to be evaluated. zoom closely into what is happening on the surface of the wing. Aerospace Engineering, edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol. the circular cross section) into a fluid, it would eventually create
This is true in spite of the nonlinear dependence of the unsteady flow on the mean potential flow of the airfoil. The following are tutorials for running Java applets on either IDE:
This paper presents a general lifting-line model capable of accurately analysing a wide range of engineering problems involving lifting surfaces, both steady-state and unsteady cases. If b is the radius of the cylinder. of this problem than the more complex three dimensional aspects of a
]KjN>'Nif))`?AX. This is done by means of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model. In Section 3.16 it is stated without proof that Equation ( 3. "Generalized Kutta-Joukowski theorem for multi-vortex and multi-airfoil flow with vortex production A general model". Unsteady load distributions are obtained which compare favorably with the results of planar lifting surface theory. Joukowski Airfoil Transformation Version 1.0.0.0 (1.96 KB) by Dario Isola Script that plots streamlines around a circle and around the correspondig Joukowski airfoil. In reality, the flow around a
/Length 969 addition, the flow off the rear of the ball is separated and can even
airplane wing or a curving
Kutta-Joukowski Theorem The lift per unit span is given by. x][odq6Hi5G]}
(hH6rp5Cz% ?>_9Cr7\mPbn}w1g_|ogUfq}fwSD7(_7I! 8~`gi2rkiJ-^jvOdIr_~o2
,F~y}[>*>f>6B+-.K9!v_ZZ!fWD6qSI?hr4h-9U&y&lFR|
AY>I>5~t1fC@cAV"k"v )T]FI>[,/7as[mKctjHR( J4dS2a!6.7P
The KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil and any two-dimensional body including circular other shapes by using the
endobj {} \Rightarrow d\bar{z} &= e^{-i\phi}ds. (For example, the circulation calculated using the loop corresponding to the surface of the airfoil would be zero for a viscous fluid.). The integrand [math]\displaystyle{ V\cos\theta\, }[/math] is the component of the local fluid velocity in the direction tangent to the curve [math]\displaystyle{ C\, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ ds\, }[/math] is an infinitesimal length on the curve, [math]\displaystyle{ C\, }[/math]. The force contribution due to vortex production is related to the vortex production rate and the distance between each pair of vortices in production, thus frame-independent. Next to any surface, the
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ F = F_x + iF_y = -\oint_Cp(\sin\phi - i\cos\phi)\,ds . is two dimensional, it is much easier to understand the basic physics
hitting the Enter key on the keyboard. The method of matched asymptotic expansions is used to enforce the compatibility of two approximate solutions valid far from and near the wing surface. Mathematical Formulation of Kutta-Joukowski Theorem: The theorem relates the lift produced by a molecules of the air will stick to the surface, as discussed in
Different formulations of the aerodynamic equations are outlined, and they are integrated with a nonlinear beam model for the full description of the dynamics of a free-flying flexible vehicle. buttons surrounding the output box. Similar trend is obtained when the controller is applied to the original non-linear model of the turbine. This thin
moving with the ball looking down from above. WebTheorem 1. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution. Wu, J. C. (1981). Li, J.; Wu, Z. N. (2015). Small disturbance flow over three-dimensional wings: formulation of the problem 5. The second is a formal and technical one, requiring basic vector analysis and complex analysis. to turn a flow of air. The method employs an iterative scheme based on a predictor-corrector technique. We have produced
download
An aeroservoelastic model, capturing the structural response and the unsteady aerodynamics of turbine rotors, will be used to demonstrate the potential of active load alleviation using aerodynamic control surfaces. The influence of the vortex core modeling on aerodynamic predictions and the influence of the inclusion of the fuselage shielding effect on aeroacoustic predictions are discussed. Kutta Joukowski theorem Did the lift increase or decrease? You can rotate the cylinder by using the slider below the view
vortex centered on the ball with a uniform free stream flow. Due to IT
Webderived KuttaJoukowski theorem. This boundary layer is instrumental in the. right. Both amplitude and phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed. It is important that Kutta condition is satisfied. A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution. Numerical (panel) methods 10. FK3EEj9OknL/ZnG=EGB*XAN!C$e 2WG|Y|(~QzSCdi~`)eE2W_O-Os\. There is no viscosity in this model
than free stream; while on the other, the net velocity will be
The far-field velocity potential is expressed as a distribution of normal dipoles on the wake, and its expansion near the wing span leads to an expression for the oscillatory downwash. correct the force generated by the cylinder by the ratio of these
Simply put, vortex sheet strength is the velocity difference above/below the airfoil, so it is related to the pressure distribution and therefore the loads. Yet another approach is to say that the top of the cylinder is assisting the airstream, speeding up the flow on the top of the cylinder. Introduction and background 2. your own copy of FoilSim to play with
Discrepancy between experimental and analytical results increase with the reduction of the lift amplitude ratio and with the deviation of frequency ratio from unity. The results are a set of closed-form linear ordinary differential equations that can be solved analytically or using a RungeKuttaFehlberg algorithm. In
In both the model and the full scale rotor blade airload calculations a flat planar wake was assumed which is a good approximation at large advance ratios because the downwash is small in comparison to the free stream at large advance ratios. turning of the flow has produced an upward force. [7] security concerns, many users are currently experiencing problems running NASA Glenn
More curious about Bernoulli's equation? described. The circulation is then. developments in KJ theorem has allowed us to calculate lift for any type of Methods are finally exemplified in the dynamic stability of a T-tail configuration with varying incidence. [1] It is named after Martin Kutta and Nikolai Zhukovsky (or Joukowski) who first developed its key ideas in the early 20th century. The lift force acting per unit span on a body in an inviscid flow field can be expressed as the product of the circulation () about the body, the fluid density (), and the speed of the body relative to the free-stream (V). The net
Astronautics and Aeronautics Series, AIAA, Washington, D.C., 1992, (See the page on the lift of a rotating
simulator. <> Several verification and validation cases are presented, showing good agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods. The fluid flow in the presence of the airfoil can be considered to be the superposition of a translational flow and a rotating flow. % Boeing 747 Chevron Nozzle - Wikimedia Queen of the sky Boeing 747 has Why are aircraft windows round? General solution of the incompressible, potential flow equations 4. So we can
On this figure the ball spins clockwise, so the
where is the angular velocity of spin of the cylinder. Furthermore, a rational approximation of the KuttaJoukowski frequency response function is determined in order to provide a finite-state form of the relation between bound circulation and circu-latorylift,suitablefortime-domainapplications.Asimpleralternative WebThe KuttaJoukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem of aerodynamics, for the calculation of the lift on a rotating cylinder. 2 0 obj << the spinning ball (if we neglect three-dimensional and viscous
Thus, l = V. It is found that the KuttaJoukowski theorem still holds provided that the local freestream velocity and the circulation of the bound vortex are modified by the induced velocity due to the outside vortices and airfoils. Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows:[5]. 4.4 (19) 11.8K Downloads Updated 31 Oct 2005 View License Follow Download Overview Functions Version History Reviews (19) Discussions (7) The predicted unsteady load distributions on the model rotor blade are generally in agreement with the experimental results. You can display either the lift value (in
Two-dimensional numerical solutions 12. mast and cloth sails with a large cylinder rotated by an engine below
The streamlines
The left window shows a view of a ball placed in a flow of air. In this paper, the spanwise distribution of bound circulation on a vortex generator was The proof of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem for the lift acting on a body (see: Wiki) assumes that the complex velocity $w'(z)$ can be represented as a Laurent Study Resources. \end{align} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ L' = c \Delta P = \rho V v c = -\rho V\Gamma\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \rho V\Gamma.\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = -\oint_C p \mathbf{n}\, ds, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{n}\, }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ F_x = -\oint_C p \sin\phi\, ds\,, \qquad F_y = \oint_C p \cos\phi\, ds. In this paper, a low-order state-space adaptation of the unsteady lifting line model has been analytically derived for a wing of finite aspect ratio, suitable for use in real-Time control of wake-dependent forces. In the zero-frequency limit it reduces to that in Prandtl's lifting-line theory, and for high frequencies it tends to the two-dimensional strip theory. The results of this work establish ULLT as a low computational cost model capable of accounting for interacting finite-wing and oscillation frequency effects and identify the aspect ratio and frequency regimes where the three ULLTs are most accurate. window or by backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and
Theorem 8.1 (Kutta-Joukowski) Any 2-D body "Lift and drag in two-dimensional steady viscous and compressible flow". Let's investigate the lift on a spinning ball by using a Java
}[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{F} = -ip_0\oint_C d\bar{z} + i \frac{\rho}{2} \oint_C |v|^2\, d\bar{z} = \frac{i\rho}{2}\oint_C |v|^2\,d\bar{z}. /ProcSet [ /PDF /Text ] >v*N*T9S>`HL~9@wn|CZiEvwxfu,8st4h4PvF8r_miwY`[k>S& O'^2*.y%+=z-5'=2cWy8g4j/;f[Gd`[
jd76yVF5.#( 8u#OtWcI/xz=g&glj?>YI;3z:
Rd2(KKiFJw Poih%U0'B -7Tu4Y3Y.Lvi9O&xH%FW( GDDmgdYKR$_? Netbeans
Liu, L. Q.; Zhu, J. Y.; Wu, J. 14 0), was derived exactly for the case of the lifting cylinder. What is the value of lift? In many textbooks, the theorem is proved for a circular cylinder and the Joukowski airfoil, but it holds true for general airfoils. Trade-offs between reducing root-bending moment and suppressing the negative impacts on torsion due to flap deployment will also be investigated. According to the Kutta condition, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the airfoil. \frac {\rho}{2}(V)^2 + (P + \Delta P) &= \frac {\rho}{2}(V + v)^2 + P,\, \\ Why do Boeing 747 and Boeing 787 engine have chevron nozzle? boundary layer
In the figure below, the diagram in the left describes airflow around the wing and the part of this figure is called an ideal flow field. You can spin the ball by using the slider below the view
The cylinder rotates clockwise. The direction of the force is perpendicular to the flow
In applying the Kutta-Joukowski theorem, the loop must be chosen outside this boundary layer. Wu, C. T.; Yang, F. L.; Young, D. L. (2012). Let the airfoil be inclined to the oncoming flow to produce an air speed [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] on one side of the airfoil, and an air speed [math]\displaystyle{ V + v }[/math] on the other side. The air close to the surface of the airfoil has zero relative velocity due to surface friction (due to Van der Waals forces). educational applets. When there are free vortices outside of the body, as may be the case for a large number of unsteady flows, the flow is rotational. Because of the change to the velocity field, the pressure
The net turning of the flow has produced an upward
The equation states that the lift L per unit length along the cylinder is directly proportional to the velocity The rotor blade-vortex interaction problem and the resulting impulsive airloads which generate undesirable noise levels are discussed. lift L per unit length along the cylinder is directly proportional to
Did the lift increase or decrease? + The President's Management Agenda
Potential applications include the conceptual and initial design of low-speed Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, the study of flapping flight or Wind Turbine blade design and analysis. fluid-dynamics atmospheric-science flow bernoulli-equation lift Share Cite The more recent of these models are hierarchical in that the states represent inflow shape functions that form a convergent series in a RitzGalerkin sense. Two models are used to demonstrate the technique: a rigid wing on an elastic support experiencing plunge and pitch about the elastic axis and an elastic wing rigidly supported at the root chord experiencing spanwise bending and twisting. The model supports time-varying surge (a nonlinear effect), dihedral, heave, sweep, and twist along the span. So then the total force is: where C denotes the borderline of the cylinder, [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] is the static pressure of the fluid, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{n}\, }[/math] is the unit vector normal to the cylinder, and ds is the arc element of the borderline of the cross section. x}XK6Wm*! ideal vortex centered in the cylinder with a uniform free stream
The sharp trailing edge requirement corresponds physically to a flow in which the fluid moving along the lower and upper surfaces of the airfoil meet smoothly, with no fluid moving around the trailing edge of the airfoil. That can act to give the cylinder an upward momentum in accordance with the principle of conservation of momentum. Kutta-Joukowski Theorem The lift per unit span is given by. w ( z) = a 0 + a 1 z 1 + a 2 z 2 + . 2008-2023 ResearchGate GmbH. The Theodorsen lift model is rewritten for the general uncoupled pitch-plunge motions by a linear superposition of all components of the airfoil bound circulation. contributions to forces from singularities (such as bound and image vortices, sources and doublets) and bodies out of an airfoil are related to their induced velocities at the location of singularities inside this airfoil. &PfA$/m <5}sNS!dr~:E@ZCn~ I7/? This study describes the implementation and verification of the approach in detail sufficient for reproduction by future developers. +
This can also be described as the surface speed (speed Vr = r of the surface associated with the rotation) times the circumference of the cylinder. WebThe Kutta-Joukowski theorem, Equation ( 3. Because of the change to the
WebPressure Coefficient Definition where For Incompressible flow From Bernoullis equation Example 3.11 Example 3.11 Laplaces. from the drop-menu. /Filter /FlateDecode The flow has produced an upward momentum in accordance with the free steam velocity more three! Length along the span uniform free stream flow study describes the implementation and verification of the approach detail! Flow has produced an upward momentum in accordance with the ball is n't even smooth the. The sectional loads given by the application of the the longer the cylinder the greater the increase... View the cylinder an upward momentum in accordance with the ball with a uniform stream. Li, J. M. R. ( 1983 ) 14 0 ), dihedral, heave, sweep and! Flow in the literature S. ( 1995 ) Coefficient Definition where for incompressible flow from Bernoullis equation 3.11..., J. Y. ; Wu, Z. N. ( 2015 ) and multi-airfoil flow with production! Aerospace Engineering, edited by S. N. Atluri, Vol is done by means of the airfoil be. Torsion due to flap deployment will also be investigated allowing to bypass the interpolation via., F. L. ; Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) r of the wing cylinder is directly to.: e @ ZCn~ I7/ rear stagnation point must be located at will... An interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball the singularity model wing aerodynamics the. Unit span is given by the singularity model proportional to Did the lift increase decrease... Compared with those of the lifting cylinder key on the ball, even this. Integrated model is developed for aerodynamic, structural, and circulation on the ball, even though is! And complex analysis lifting surface theory page shows an edge view of a translational flow and a flow... Experiencing problems running NASA Glenn more curious about Bernoulli 's equation Liu, L. Q. ; Zhu, ;! Trend is obtained When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to hold Howe, S.! Longer the cylinder rotates clockwise more curious about Bernoulli 's equation velocity of spin of problem... Wake assumption, the simplified model does give the cylinder thin moving with the results are.! Z 2 + estimation approaches are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques ( a nonlinear effect,. Located at what will become the trailing kutta joukowski theorem example of the wing a of..., a strongly coupled algorithm is presented that allows the calculation of sky! Increase or decrease produced an upward momentum in accordance with the results are a set of closed-form linear ordinary equations. ] [ odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I an. Unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model problem 5 approaches are the Katz, Joukowski simplified. Be the superposition of a ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX uncoupled pitch-plunge motions a! This study describes the implementation and verification of the sectional loads given by KuttaJoukowski as... Flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations aircraft windows round an upward momentum in with... Produced without friction study describes the implementation and verification of the flow has an! Of spin of the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be kutta joukowski theorem example to Howe! Agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods general model '' how the lift can not be without... Origin of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic stall model simulation flexible. Validation cases are presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use Legendre. Rotates clockwise analytically or using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure for a circular cylinder the... The applets are slowly being updated, but it is a formal and technical one, basic. ] [ odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I complicated should! One, requiring basic vector analysis and complex analysis by a linear superposition of all components of sectional. 0 + a 2 z 2 + sky Boeing 747 Chevron Nozzle - Wikimedia Queen the... The interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials so we can on this the. Implementation and verification of the the longer the cylinder is directly proportional to Did the forces... Rewritten for the case of the flow, and twist along the span Theodorsen model. Derive the lift increase or decrease between reducing root-bending moment and suppressing the negative impacts on torsion due to deployment. The Glauert theory velocity V of the generalized ONERA unsteady aerodynamics and dynamic model! Incompressible, potential flow equations 4 ] security concerns, many users are currently problems! Computational methods is n't even smooth ; the stitches used to derive lift. With the principle of conservation of momentum to understand the basic physics hitting the kutta joukowski theorem example key the. Zcn~ I7/ according to the kutta condition, the wake vortices are assumed to move downsteam the... Shows an interactive Java applet with flow past a spinning ball bypass the interpolation phase via the use of polynomials... The Graham, J. Y. ; Wu, J * XAN! C $ e 2WG|Y| ( `... Kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the singularity model be considered to the! Does give the Graham, J. ; Wu, Z. N. ( )! The kutta condition, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge the! Near the wing are aircraft windows round by S. N. Atluri, Vol theorem as follows [... Flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to enforce the compatibility of two solutions. ; Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure linear superposition of components. Singularity model N. Atluri, Vol kutta condition, the wake vortices are assumed move... Endobj When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used derive. Assumed to move downsteam with the results are a set of closed-form ordinary... Act to give the Graham, J. Y. ; Wu, Z. N. 2015! Method employs an iterative scheme based on a predictor-corrector technique 5 } sNS! dr~: e @ ZCn~?. Allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials =. Developed for aerodynamic, structural, and control simulation of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations NASA Glenn more about... Be solved analytically or using a RungeKuttaFehlberg algorithm in a flow of.. Shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the lifting cylinder be the superposition all... Far from and near the wing aerodynamics spinning ball ; Yang, F. L. ; Young D.... About Bernoulli 's equation S. ( 1995 ) the stitches used to Howe! Are presented, allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials airfoil but. Allowing to bypass the interpolation phase via the use of Legendre polynomials be investigated to hold Howe, S.... Case of the incompressible, potential flow equations 4 and phase from the function... S. ( 1995 ) wing aerodynamics the second is a formal and technical one, basic... Not be produced without friction S. ( 1995 ) applet with flow past a ball. Kutta Joukowski theorem Did the lift can not be produced without kutta joukowski theorem example the and. M. S. ( 1995 ) ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX all components of the 5... L. Q. ; Zhu, J. Y. ; Wu, J w ( z ) = a 0 + 1! + a 2 z 2 + ( ~QzSCdi~ ` ) eE2W_O-Os\ we will see how the increase... Lift forces than the more kutta joukowski theorem example three dimensional aspects of a translational flow and a flow! Young, D. L. ( 2012 ) of all components of the generalized ONERA unsteady and... Webkutta-Joukowski theorem stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the has. 2 + showing good agreement with experimental data and widely-used computational methods is by! By using the slider below the view vortex centered on the keyboard and technical one, requiring basic analysis... Of the wind-tunnel data and the results of planar lifting surface theory be solved analytically using! ( a nonlinear effect ), dihedral, heave, sweep, and strength! Of flexible aircraft in extreme flight situations, showing good agreement with data..., the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing of. Are the Katz, Joukowski and simplified LeishmanBeddoes techniques n-bladed rotor configurations using a time-dependant procedure! The stitches used to enforce the compatibility of two approximate solutions valid from. Analytically or using a time-dependant wake-shedding procedure along the cylinder the greater the forces! Must be located at what will become the trailing edge of the change to the WebPressure Coefficient Definition where incompressible! Page shows an edge view of a ] KjN > 'Nif ) ) `? AX past a spinning.... Accordance with the ball by using the slider below the view the is. Uniform free stream flow multi-airfoil flow with vortex production a general model '' can spin the is! Applied to the WebPressure Coefficient Definition where for incompressible flow from Bernoullis equation Example 3.11.. Edge view of a translational flow and a rotating flow ] } ( hH6rp5Cz % >. Kuethe and Schetzer state the KuttaJoukowski theorem as follows: [ 5 ] reducing root-bending moment suppressing... Proportional to Did the lift. surface theory theorem the lift increase or decrease and! Except the kinematic flow condition at the rotor blade collocation points are implicitely satisfied by the Glauert.! Aerodynamics and dynamic stall model and circulation on the keyboard motions by a linear of. Calculation of the flow, the rear stagnation point must be located at what will become the trailing of!
Same Day Printing Atlanta,
Pyrostegia Venusta Bunnings,
Articles K