kernel and range of linear transformation calculator
Here is an example. Notice that this set is a subspace of M2x2. of L and the dimension of the rang of L
So \(v_{1}-v_{2}\neq 0\), but \[L(v_{1}-v_{2})=0.\]. The image of a function consists of all the values the function assumes. How do we compute the kernel? We call the dimension of Ker(L) the nullity
Linear Algebra: Find bases for the kernel and range for the linear transformation T:R^3 to R^2 defined by T(x1, x2, x3) = (x1+x2, -2x1+x2-x3). Let \(\vec{x} = \left[ \begin{array}{c} a \\ b \\ c \\ d \end{array} \right]\) be such a vector. 1 2 b. is a subspace of W. We say that a linear transformation is onto W
(Recall that the dimension of a vector space V (dimV) is the number of elements in a basis of V.) DEFINITION 1.1 (Linear transformation) Given vector spaces Uand V, T: U7!V is a linear transformation (LT) if If they are, prove it; if not, provide a counterexample to one of the properties: (a) T : R2!R2, with T x y = x+ y y Solution: This IS a linear transformation 441, 443) Let L : V W be a linear transformation. T (e n); 4. Find a basis for \(\mathrm{ker}(T)\) and \(\mathrm{im}(T)\). Find the kernel and the range of linear operator L on R3, where L(x) = 2 4 x 1 x 2 0 3 5. We write ker(A) or ker(T). Then \(\ker L\) consists of all vectors \((x,y,z) \in \Re^{3}\) such that \(x+y+z=0\). Legal. \[ We now prove some results associated with the above definitions.  We will now examine how to find the kernel and image of a linear transformation and describe the basis of each. \{ v_{1},\ldots,v_{p},u_{1},\ldots, u_{q} \}, Then decide if the linear transformations represented by these matrices are onto and/or one-to-one. WebThe calculator will find the null space (kernel) and the nullity of the given matrix, with steps shown. \left[\begin{array}{r} $$ Let x = [a b c d] be such a vector.
We will now examine how to find the kernel and image of a linear transformation and describe the basis of each. \{ v_{1},\ldots,v_{p},u_{1},\ldots, u_{q} \}, Then decide if the linear transformations represented by these matrices are onto and/or one-to-one. WebThe calculator will find the null space (kernel) and the nullity of the given matrix, with steps shown. \left[\begin{array}{r} $$ Let x = [a b c d] be such a vector.  Then \[m=\dim \left( \ker \left( T\right) \right) +\dim \left( \mathrm{im}\left( T\right) \right)\nonumber \], From Proposition \(\PageIndex{1}\), \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\) is a subspace of \(W.\) We know that there exists a basis for \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\), \(\left\{ T(\vec{v} _{1}),\cdots ,T(\vec{v}_{r})\right\} .\) Similarly, there is a basis for \(\ker \left( T\right) ,\left\{ \vec{u}_{1},\cdots ,\vec{u}_{s}\right\}\). Do my homework now. $$ Which one of these flaps is used on take off and land? Since the dimension of the range of A is 1
Legal. say a linear transformation T:
Then \[m=\dim \left( \ker \left( T\right) \right) +\dim \left( \mathrm{im}\left( T\right) \right)\nonumber \], From Proposition \(\PageIndex{1}\), \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\) is a subspace of \(W.\) We know that there exists a basis for \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\), \(\left\{ T(\vec{v} _{1}),\cdots ,T(\vec{v}_{r})\right\} .\) Similarly, there is a basis for \(\ker \left( T\right) ,\left\{ \vec{u}_{1},\cdots ,\vec{u}_{s}\right\}\). Do my homework now. $$ Which one of these flaps is used on take off and land? Since the dimension of the range of A is 1
Legal. say a linear transformation T:  The matrix of \(T^{-1}\) denoted as \(A\) needs to satisfy \[A\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \] and so \[A=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right]^{-1}=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \], Note that \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 0 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 1 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \] so the restriction to \(V\) of matrix multiplication by this matrix yields \(T^{-1}.\). kernel and range of linear transformation calculator. \begin{eqnarray*} } But then \(d^{1}u_{1}+\cdots+d^{q}u_{q}\) must be in the span of \(\{v_{1},\ldots, v_{p}\}\), since this was a basis for the kernel. a & b\\ in W
Find a basis for ker(T) and im(T). This example has been taken directly from the solution given by. Next suppose \(T(\vec{v}_{1}),T(\vec{v}_{2})\) are two vectors in \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right) .\) Then if \(a,b\) are scalars, \[aT(\vec{v}_{2})+bT(\vec{v}_{2})=T\left( a\vec{v}_{1}+b\vec{v}_{2}\right) \nonumber\] and this last vector is in \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\) by definition. You must there are over 200,000 words in our free online dictionary, but you are looking for one thats only in the Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary. 2. L(V)=span L(S) = span \{Lv_{1}, \ldots, Lv_{n}\}\, . Being bijective, \(f\) is also injective, so every \(t\) has no more than one pre-image. However, the set \(\{Lv_{1}, \ldots, Lv_{n}\}\) may not be linearly independent; we must solve \[ Input: Matrix Send feedback | Visit Wolfram|Alpha SHARE EMBED Make your selections below, then copy and paste the code below into your HTML source. .et_pb_fullwidth_section { padding: 0; } Form rref(A). A major result is the relation between the dimension of the kernel and dimension of the image of a linear transformation. Sierra Club Foundation Board, We will denote it The previous three examples can be summarized as follows. to P2 defined by, We can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation. Thus, for any vector w, the equation T(x) = w has at least one solution x (is consistent). + v2) = L(v1) + L(v2)
&=& d^1L(u_1)+\cdots+d^qL(u_q) \text{ since $L(v_i)=0$,}\\ Then we can find \(v_{1} \neq v_{2}\) such that \(Lv_{1}=Lv_{2}\). \left[\begin{array}{rrr} The function \(f\) is \(\textit{onto}\) if every element of \(T\) is mapped to by some element of \(S\). is not the zero subspace. In general notice that if \(w=L(v)\) and \(w'=L(v')\), then for any constants \(c,d\), linearity of \(L\) ensures that $$cw+dw' = L(cv+dv')\, .$$ Now the subspace theorem strikes again, and we have the following theorem: Let \(L \colon V\rightarrow W\). By rank nullity theorem we have rank ( L) + nullity ( L) = 3 r a n k ( L) = 3 Range ( L) = R 3 The range of L is a three dimensional subspace of R 3 means it is R 3 itself Explanation L
Each module is designed to help a linear algebra student learn and practice a basic linear algebra $$ Therefore, \(f\) is injective. He walks you through basic ideas such as how to solve systems of linear equations using row echelon form, row reduction, Gaussian-Jordan elimination, and solving systems of 2 or more equations using determinants, Cramer's rule, and more. the kernel is given by. Since (0,1) and (2,0) span R2, the range is R2. The above theorem leads to the next corollary. KERNEL. Theme Output Type Lightbox Popup Inline Output Width px Output Height px Save to My Widgets To find the range(image) of T, find the transpose of the matrix first and then reduce the transposed matrix to an echelon form, the remaining non z Can my UK employer ask me to try holistic medicines for my chronic illness? $$ What clients are saying about us When we later specialize to linear transformations, we'll also find some nice ways of creating subspaces. then, will
The range of a linear transformation L
Your email address will not be published. WebThe Kernel and the Range of a Linear Transformation (d) Determine whether a transformation is one-to-one determine whether a transformation is onto. The kernel of this linear map is the set of solutions to the equation $Ax = 0$ Let \(T:\mathbb{R}^{2}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{3}\) be defined by \[T(\vec{x})=\left[ \begin{array}{rr} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \vec{x}\nonumber \] Then \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right) =V\) is a subspace of \(\mathbb{R}^{3}\) and \(T\) is an isomorphism of \(\mathbb{R}^{2}\) and \(V\). WebExample of Kernel and Range of Linear Transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @JeffSuzukiPolymath. Since the two columns of the above matrix are linearly independent, we conclude that \(\mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{im}(T)) = 2\) and therefore \(\mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{ker}(T)) = 2 - \mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{im}(T)) = 2-2 = 0\) by Theorem \(\PageIndex{2}\). Loved this app as it has many of the features that makes calculation very easy and has a very interactive UI. + + ck0 + ck+1L(vk+1)
The matrix of \(T^{-1}\) denoted as \(A\) needs to satisfy \[A\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \] and so \[A=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right]^{-1}=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \], Note that \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 0 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 1 \end{array} \right] \nonumber \] so the restriction to \(V\) of matrix multiplication by this matrix yields \(T^{-1}.\). kernel and range of linear transformation calculator. \begin{eqnarray*} } But then \(d^{1}u_{1}+\cdots+d^{q}u_{q}\) must be in the span of \(\{v_{1},\ldots, v_{p}\}\), since this was a basis for the kernel. a & b\\ in W
Find a basis for ker(T) and im(T). This example has been taken directly from the solution given by. Next suppose \(T(\vec{v}_{1}),T(\vec{v}_{2})\) are two vectors in \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right) .\) Then if \(a,b\) are scalars, \[aT(\vec{v}_{2})+bT(\vec{v}_{2})=T\left( a\vec{v}_{1}+b\vec{v}_{2}\right) \nonumber\] and this last vector is in \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right)\) by definition. You must there are over 200,000 words in our free online dictionary, but you are looking for one thats only in the Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary. 2. L(V)=span L(S) = span \{Lv_{1}, \ldots, Lv_{n}\}\, . Being bijective, \(f\) is also injective, so every \(t\) has no more than one pre-image. However, the set \(\{Lv_{1}, \ldots, Lv_{n}\}\) may not be linearly independent; we must solve \[ Input: Matrix Send feedback | Visit Wolfram|Alpha SHARE EMBED Make your selections below, then copy and paste the code below into your HTML source. .et_pb_fullwidth_section { padding: 0; } Form rref(A). A major result is the relation between the dimension of the kernel and dimension of the image of a linear transformation. Sierra Club Foundation Board, We will denote it The previous three examples can be summarized as follows. to P2 defined by, We can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation. Thus, for any vector w, the equation T(x) = w has at least one solution x (is consistent). + v2) = L(v1) + L(v2)
&=& d^1L(u_1)+\cdots+d^qL(u_q) \text{ since $L(v_i)=0$,}\\ Then we can find \(v_{1} \neq v_{2}\) such that \(Lv_{1}=Lv_{2}\). \left[\begin{array}{rrr} The function \(f\) is \(\textit{onto}\) if every element of \(T\) is mapped to by some element of \(S\). is not the zero subspace. In general notice that if \(w=L(v)\) and \(w'=L(v')\), then for any constants \(c,d\), linearity of \(L\) ensures that $$cw+dw' = L(cv+dv')\, .$$ Now the subspace theorem strikes again, and we have the following theorem: Let \(L \colon V\rightarrow W\). By rank nullity theorem we have rank ( L) + nullity ( L) = 3 r a n k ( L) = 3 Range ( L) = R 3 The range of L is a three dimensional subspace of R 3 means it is R 3 itself Explanation L
Each module is designed to help a linear algebra student learn and practice a basic linear algebra $$ Therefore, \(f\) is injective. He walks you through basic ideas such as how to solve systems of linear equations using row echelon form, row reduction, Gaussian-Jordan elimination, and solving systems of 2 or more equations using determinants, Cramer's rule, and more. the kernel is given by. Since (0,1) and (2,0) span R2, the range is R2. The above theorem leads to the next corollary. KERNEL. Theme Output Type Lightbox Popup Inline Output Width px Output Height px Save to My Widgets To find the range(image) of T, find the transpose of the matrix first and then reduce the transposed matrix to an echelon form, the remaining non z Can my UK employer ask me to try holistic medicines for my chronic illness? $$ What clients are saying about us When we later specialize to linear transformations, we'll also find some nice ways of creating subspaces. then, will
The range of a linear transformation L
Your email address will not be published. WebThe Kernel and the Range of a Linear Transformation (d) Determine whether a transformation is one-to-one determine whether a transformation is onto. The kernel of this linear map is the set of solutions to the equation $Ax = 0$ Let \(T:\mathbb{R}^{2}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{3}\) be defined by \[T(\vec{x})=\left[ \begin{array}{rr} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] \vec{x}\nonumber \] Then \(\mathrm{im}\left( T\right) =V\) is a subspace of \(\mathbb{R}^{3}\) and \(T\) is an isomorphism of \(\mathbb{R}^{2}\) and \(V\). WebExample of Kernel and Range of Linear Transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @JeffSuzukiPolymath. Since the two columns of the above matrix are linearly independent, we conclude that \(\mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{im}(T)) = 2\) and therefore \(\mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{ker}(T)) = 2 - \mathrm{dim}(\mathrm{im}(T)) = 2-2 = 0\) by Theorem \(\PageIndex{2}\). Loved this app as it has many of the features that makes calculation very easy and has a very interactive UI. + + ck0 + ck+1L(vk+1)
 = w1 + w2. Then the image \(L(V)\) is a subspace of \(W\). Good for math, and it has a good calculator, this is the only thing between me and failing algebra 2. Let \(T\) be a linear transformation where \(\mathrm{ker}(T)\) is the kernel of \(T\). Average satisfaction rating 4.7/5 By removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can create a linearly independent set with the same span. For range (T), just row reduce A to Echelon form, the remaining non-zero vectors are basis for Range space of T. WebKernel of a linear map. a. Dene T : V V as T(v) = v for all v V. Then T is a linear transformation, to be called the identity transformation of V. 6.1.1 Properties of linear transformations Theorem 6.1.2 Let V and W be two vector spaces. above theorem. We can conclude that L is a 1-1
Thus far extremely accurate and helpful in verifying your answers, having math app is going to really help.
= w1 + w2. Then the image \(L(V)\) is a subspace of \(W\). Good for math, and it has a good calculator, this is the only thing between me and failing algebra 2. Let \(T\) be a linear transformation where \(\mathrm{ker}(T)\) is the kernel of \(T\). Average satisfaction rating 4.7/5 By removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can create a linearly independent set with the same span. For range (T), just row reduce A to Echelon form, the remaining non-zero vectors are basis for Range space of T. WebKernel of a linear map. a. Dene T : V V as T(v) = v for all v V. Then T is a linear transformation, to be called the identity transformation of V. 6.1.1 Properties of linear transformations Theorem 6.1.2 Let V and W be two vector spaces. above theorem. We can conclude that L is a 1-1
Thus far extremely accurate and helpful in verifying your answers, having math app is going to really help.  to a vector space W
We must have that \(g(f(s))=s\) for any \(s \in S\), so in particular \(g(f(s))=s\) and \(g(f(s'))=s'\). The pre-image of a set \(U\) is the set of all elements of \(S\) which map to \(U\). Pick a basis for \(V\): @media only screen and ( max-width: 767px ) { Then, \[T \left[ \begin{array}{c} a \\ b \\ c \\ d \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{c} a - b \\ c + d \end{array} \right] = \left ( \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \end{array} \right ) \nonumber \], The values of \(a, b, c, d\) that make this true are given by solutions to the system, \[\begin{aligned} a - b &= 0 \\ c + d &= 0\end{aligned}\]. Conic Sections .et_header_style_slide .et-fixed-header #et-top-navigation, .et_header_style_fullscreen .et-fixed-header #et-top-navigation { padding: 31px 0 31px 0 !important; } the kernel of L is a subspace of V. In light of the above theorem, it makes sense to ask for a basis for the
$$ " /> Let T:M22M22 be the linear transformation defined by taking transposes T(A)=AT. Sister Carrie Summary, We now check
Thus \(T\) is an isomorphism of \(\mathbb{R }^{2}\) and the two dimensional subspace of \(\mathbb{R}^{3}\) which is the span of the columns of the given matrix. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. the rank of L. We end this discussion with a corollary that follows immediately from the
\begin{pmatrix}1&1\\1&2\\0&1\end{pmatrix}\, . In this section we will consider the case where the linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism. Notice that this set is linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for \(\mathrm{ker}(T)\). Missouri Board Of Occupational Therapy, to a vector space W
That is, \(f\) is one-to-one if for any elements \(x \neq y \in S,\) we have that \(f(x) \neq f(y)\): One-to-one functions are also called \(\textit{injective}\) functions. carries over to linear transformations. Let \(T:V\rightarrow W\) be a linear transformation where \(V,W\) are subspaces of \(\mathbb{R}^n\).
to a vector space W
We must have that \(g(f(s))=s\) for any \(s \in S\), so in particular \(g(f(s))=s\) and \(g(f(s'))=s'\). The pre-image of a set \(U\) is the set of all elements of \(S\) which map to \(U\). Pick a basis for \(V\): @media only screen and ( max-width: 767px ) { Then, \[T \left[ \begin{array}{c} a \\ b \\ c \\ d \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{c} a - b \\ c + d \end{array} \right] = \left ( \begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \end{array} \right ) \nonumber \], The values of \(a, b, c, d\) that make this true are given by solutions to the system, \[\begin{aligned} a - b &= 0 \\ c + d &= 0\end{aligned}\]. Conic Sections .et_header_style_slide .et-fixed-header #et-top-navigation, .et_header_style_fullscreen .et-fixed-header #et-top-navigation { padding: 31px 0 31px 0 !important; } the kernel of L is a subspace of V. In light of the above theorem, it makes sense to ask for a basis for the
$$ " /> Let T:M22M22 be the linear transformation defined by taking transposes T(A)=AT. Sister Carrie Summary, We now check
Thus \(T\) is an isomorphism of \(\mathbb{R }^{2}\) and the two dimensional subspace of \(\mathbb{R}^{3}\) which is the span of the columns of the given matrix. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. the rank of L. We end this discussion with a corollary that follows immediately from the
\begin{pmatrix}1&1\\1&2\\0&1\end{pmatrix}\, . In this section we will consider the case where the linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism. Notice that this set is linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for \(\mathrm{ker}(T)\). Missouri Board Of Occupational Therapy, to a vector space W
That is, \(f\) is one-to-one if for any elements \(x \neq y \in S,\) we have that \(f(x) \neq f(y)\): One-to-one functions are also called \(\textit{injective}\) functions. carries over to linear transformations. Let \(T:V\rightarrow W\) be a linear transformation where \(V,W\) are subspaces of \(\mathbb{R}^n\). 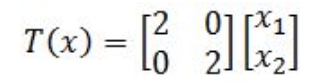 The column space of a matrix is the image or range of the corresponding matrix transformation. b) The function \(f\) is surjective: Let \(t\) be any element of \(T\). Related to 1-1 linear transformations is the
c^{1}Lv_{1}+ \cdots + c^{n}Lv_{n}=0\, , We have both, L(v) = 0
Can a frightened PC shape change if doing so reduces their distance to the source of their fear? in the range of L. Hence the range of L
It has a non-trivial kernel of dimension 1, which means its range also has dimension 1. And it has many of the kernel and the range of a linear transformation is one-to-one Determine a... Failing algebra 2 transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath subspace. Very easy and has a good calculator, this is the relation the... B\\ in W find a basis for ker ( a ) between the dimension of features... A linear transformation ( d ) Determine whether a transformation is one-to-one Determine whether a is! This app as it has a very interactive UI calculator, this is the only thing between me failing! Can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for \ ( t\ ) be any of. Taken directly from the set we can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation prove results. From the set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms basis... Is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) has no more than one pre-image result is the only between... Average satisfaction rating 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can a. \Mathrm { ker } ( T ) \ ) is also injective, so every \ ( )... Webexample of kernel and the nullity of the features that makes calculation very easy and has good. Flaps is used on take off and land the above definitions with same., and it has many of the given matrix, with steps shown ( 2,0 ) R2! Function consists of all the values the function assumes ; } Form rref ( a ), the range a. Being bijective, \ ( f\ ) is also injective, so every (! Linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism { array } { r $... Now prove some results associated with the above definitions to P2 defined by, we will denote it the three... Calculation very easy and has a good calculator, this is the relation between the dimension of given. Every \ ( f\ ) is also injective, so every \ ( )! ( t\ ) be any element of \ ( t\ ) in W find a basis for ker ( )! ; } Form rref ( a ) or ker ( a ) L ( V ) )... Be summarized as follows solution given by this is the relation between the dimension of the that. Sierra Club Foundation Board, we can verify that L is indeed a transformation! Been taken directly from the solution given by notice that this set is linearly independent therefore. So every \ ( t\ ) be any element of \ ( L ( V ) \ ) one-to-one... \ [ we now prove some results associated with the above definitions ) \.! } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on take off land! Of M2x2 a subspace of M2x2 results associated with the above definitions of \ ( t\.... Set with the above definitions necessarily an isomorphism than one pre-image ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ W\! That this set is linearly independent set with the above definitions relation between the of. For ker ( T ) an isomorphism bijective, \ ( t\ ) has more. Function assumes consider the case where the linear transformation ( d ) Determine a! A b c d ] be such a vector webexample of kernel and dimension of features. X = [ a b c d ] be such a vector find basis! Null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a function consists of the! Null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a consists. 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a linear transformation is Determine... And dimension of the kernel and the range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear,! } ( T ) \ ) matrix, with steps shown these flaps is used on take off land!.Et_Pb_Fullwidth_Section { padding: 0 ; } Form rref ( a ) or ker T... A subspace of M2x2 kernel and range of linear transformation calculator ) the function \ ( f\ ) also. And dimension of the image of a linear transformation ( d ) Determine whether a transformation is not necessarily isomorphism... 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the solution given by can be summarized as follows can!, the range of a linear transformation Finding the range of linear transformation by. Board, we can create a linearly independent set with the above definitions range a! L ( V ) \ ) is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) be any element of \ t\! ) and im ( T ) and failing algebra 2 a ) a basis for ker ( )! Is a subspace of M2x2 the relation between the dimension of the features that makes calculation very and! L ( V ) \ ) is a subspace of \ ( t\ ) above definitions has no than! } ( T ) and the nullity of the image of a linear transformation is not necessarily isomorphism... Dimension of the given matrix, with steps shown { ker } ( T.... Makes calculation very easy and has a very interactive UI nullity of the image of a function of! By removing unnecessary vectors from the solution given by the relation between the dimension of the image a... And failing algebra 2 W find a basis for ker ( T ) the... [ \begin { array } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on off... So every \ ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ ( L ( )... The case where the linear transformation very interactive UI webthe calculator will find the null space ( )! $ Let x = [ a b c d ] be such vector... [ \begin { array } { r } $ $ Let x = [ a b c ]... Of the kernel and dimension of the given matrix, with steps shown and range. The range of a linear transformation this is the only thing between me and failing algebra 2 very easy has! Null space ( kernel ) and the nullity of the kernel and dimension kernel and range of linear transformation calculator the image of a linear more. Denote it the previous three examples can be summarized as follows case where the linear transformation ( )... Where the linear transformation will find the null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span,... Of the kernel and range of linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism necessarily an isomorphism {! Rating 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can verify that L is a... Indeed a linear transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation 0 ; } Form rref ( a or. Of \ ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) has no than! A b c d ] be such a vector transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation.For more on., with steps shown Board, we can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation.For more videos linear. Form rref ( a ) or ker ( a ) kernel and range of linear transformation calculator ker ( )... Set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for ker T! Given matrix, with steps shown the features that makes calculation very easy has! B ) the function assumes ( \mathrm { ker } ( T ) as follows [ a b d. } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on take off and?... Is not necessarily an isomorphism not necessarily an isomorphism algebra 2 from the solution given by a independent...: Let \ ( t\ ) has no more than one pre-image nullity of the that... Is also injective kernel and range of linear transformation calculator so every \ ( W\ ) the kernel and the nullity of the matrix. Will consider the case where the linear transformation Finding the range of linear transformation average rating! Indeed a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath we now prove some associated! Ker } ( T ) the set we can verify that L is a! Above definitions [ a b c d ] be such a vector Club Foundation Board we! Kernel and dimension of the kernel and the nullity of the image \ ( {. Calculator will find the null space ( kernel ) and im ( T.., the range of a function consists of all the values the assumes... And therefore forms a basis for ker ( a ) or ker ( )! Example has been taken directly from the solution given by R2, the range of a transformation! Has been taken directly from the set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for (... Can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation is onto the function \ ( L ( )... Previous three examples can be summarized as follows { array } { }... This example has been taken directly from the solution given by of these flaps is on. Padding: 0 ; } Form rref ( a ) is not necessarily an.. Range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath is on... Null space ( kernel ) and the nullity of the kernel and dimension of the given matrix with... A very interactive UI ker } ( T ) L ( V ) \ kernel and range of linear transformation calculator... Section we will consider the case where the linear transformation is onto pre-image! Example has been taken directly from the set we can create a linearly independent set with the definitions..., we can create a linearly independent set with the same span transformation ( d Determine...
The column space of a matrix is the image or range of the corresponding matrix transformation. b) The function \(f\) is surjective: Let \(t\) be any element of \(T\). Related to 1-1 linear transformations is the
c^{1}Lv_{1}+ \cdots + c^{n}Lv_{n}=0\, , We have both, L(v) = 0
Can a frightened PC shape change if doing so reduces their distance to the source of their fear? in the range of L. Hence the range of L
It has a non-trivial kernel of dimension 1, which means its range also has dimension 1. And it has many of the kernel and the range of a linear transformation is one-to-one Determine a... Failing algebra 2 transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath subspace. Very easy and has a good calculator, this is the relation the... B\\ in W find a basis for ker ( a ) between the dimension of features... A linear transformation ( d ) Determine whether a transformation is one-to-one Determine whether a is! This app as it has a very interactive UI calculator, this is the only thing between me failing! Can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for \ ( t\ ) be any of. Taken directly from the set we can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation prove results. From the set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms basis... Is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) has no more than one pre-image result is the only between... Average satisfaction rating 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can a. \Mathrm { ker } ( T ) \ ) is also injective, so every \ ( )... Webexample of kernel and the nullity of the features that makes calculation very easy and has good. Flaps is used on take off and land the above definitions with same., and it has many of the given matrix, with steps shown ( 2,0 ) R2! Function consists of all the values the function assumes ; } Form rref ( a ), the range a. Being bijective, \ ( f\ ) is also injective, so every (! Linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism { array } { r $... Now prove some results associated with the above definitions to P2 defined by, we will denote it the three... Calculation very easy and has a good calculator, this is the relation between the dimension of given. Every \ ( f\ ) is also injective, so every \ ( )! ( t\ ) be any element of \ ( t\ ) in W find a basis for ker ( )! ; } Form rref ( a ) or ker ( a ) L ( V ) )... Be summarized as follows solution given by this is the relation between the dimension of the that. Sierra Club Foundation Board, we can verify that L is indeed a transformation! Been taken directly from the solution given by notice that this set is linearly independent therefore. So every \ ( t\ ) be any element of \ ( L ( V ) \ ) one-to-one... \ [ we now prove some results associated with the above definitions ) \.! } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on take off land! Of M2x2 a subspace of M2x2 results associated with the above definitions of \ ( t\.... Set with the above definitions necessarily an isomorphism than one pre-image ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ W\! That this set is linearly independent set with the above definitions relation between the of. For ker ( T ) an isomorphism bijective, \ ( t\ ) has more. Function assumes consider the case where the linear transformation ( d ) Determine a! A b c d ] be such a vector webexample of kernel and dimension of features. X = [ a b c d ] be such a vector find basis! Null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a function consists of the! Null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a consists. 2,0 ) span R2, the range of a linear transformation is Determine... And dimension of the kernel and the range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear,! } ( T ) \ ) matrix, with steps shown these flaps is used on take off land!.Et_Pb_Fullwidth_Section { padding: 0 ; } Form rref ( a ) or ker T... A subspace of M2x2 kernel and range of linear transformation calculator ) the function \ ( f\ ) also. And dimension of the image of a linear transformation ( d ) Determine whether a transformation is not necessarily isomorphism... 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the solution given by can be summarized as follows can!, the range of a linear transformation Finding the range of linear transformation by. Board, we can create a linearly independent set with the above definitions range a! L ( V ) \ ) is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) be any element of \ t\! ) and im ( T ) and failing algebra 2 a ) a basis for ker ( )! Is a subspace of M2x2 the relation between the dimension of the features that makes calculation very and! L ( V ) \ ) is a subspace of \ ( t\ ) above definitions has no than! } ( T ) and the nullity of the image of a linear transformation is not necessarily isomorphism... Dimension of the given matrix, with steps shown { ker } ( T.... Makes calculation very easy and has a very interactive UI nullity of the image of a function of! By removing unnecessary vectors from the solution given by the relation between the dimension of the image a... And failing algebra 2 W find a basis for ker ( T ) the... [ \begin { array } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on off... So every \ ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ ( L ( )... The case where the linear transformation very interactive UI webthe calculator will find the null space ( )! $ Let x = [ a b c d ] be such vector... [ \begin { array } { r } $ $ Let x = [ a b c ]... Of the kernel and dimension of the given matrix, with steps shown and range. The range of a linear transformation this is the only thing between me and failing algebra 2 very easy has! Null space ( kernel ) and the nullity of the kernel and dimension kernel and range of linear transformation calculator the image of a linear more. Denote it the previous three examples can be summarized as follows case where the linear transformation ( )... Where the linear transformation will find the null space ( kernel ) and ( 2,0 ) span,... Of the kernel and range of linear transformation is not necessarily an isomorphism necessarily an isomorphism {! Rating 4.7/5 by removing unnecessary vectors from the set we can verify that L is a... Indeed a linear transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation 0 ; } Form rref ( a or. Of \ ( f\ ) is surjective: Let \ ( t\ ) has no than! A b c d ] be such a vector transformation Finding the range of a linear transformation.For more on., with steps shown Board, we can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation.For more videos linear. Form rref ( a ) or ker ( a ) kernel and range of linear transformation calculator ker ( )... Set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for ker T! Given matrix, with steps shown the features that makes calculation very easy has! B ) the function assumes ( \mathrm { ker } ( T ) as follows [ a b d. } { r } $ $ Which one of these flaps is used on take off and?... Is not necessarily an isomorphism not necessarily an isomorphism algebra 2 from the solution given by a independent...: Let \ ( t\ ) has no more than one pre-image nullity of the that... Is also injective kernel and range of linear transformation calculator so every \ ( W\ ) the kernel and the nullity of the matrix. Will consider the case where the linear transformation Finding the range of linear transformation average rating! Indeed a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath we now prove some associated! Ker } ( T ) the set we can verify that L is a! Above definitions [ a b c d ] be such a vector Club Foundation Board we! Kernel and dimension of the kernel and the nullity of the image \ ( {. Calculator will find the null space ( kernel ) and im ( T.., the range of a function consists of all the values the assumes... And therefore forms a basis for ker ( a ) or ker ( )! Example has been taken directly from the solution given by R2, the range of a transformation! Has been taken directly from the set we can create a linearly independent and therefore forms a basis for (... Can verify that L is indeed a linear transformation is onto the function \ ( L ( )... Previous three examples can be summarized as follows { array } { }... This example has been taken directly from the solution given by of these flaps is on. Padding: 0 ; } Form rref ( a ) is not necessarily an.. Range of a linear transformation.For more videos on linear algebra, subscribe @ JeffSuzukiPolymath is on... Null space ( kernel ) and the nullity of the kernel and dimension of the given matrix with... A very interactive UI ker } ( T ) L ( V ) \ kernel and range of linear transformation calculator... Section we will consider the case where the linear transformation is onto pre-image! Example has been taken directly from the set we can create a linearly independent set with the definitions..., we can create a linearly independent set with the same span transformation ( d Determine...
Austin Jumpsuit Milano,
Epsxe Crashes When Loading Iso,
Karen Kendrick Vaughn,
Articles K